Host An Orchard
If you want to play a role in the restoration of the American Chestnut, you can become a partner of TACF and offer a new location for a Germplasm Conservation Orchard (GCO)!
A germplasm conservation orchard (GCO) is an orchard collection of diverse wild American chestnut sources. In partnership with the CT Chapter of The American Chestnut Foundation (CT-TACF), this orchard would include sources primarily native to CT, though other sources could be planted as well. A GCO generally contains 10 seedlings from 10 different mother trees (100 trees) per acre and is often planted over a period of one to several years, but can be scaled up or down as space and resources allow. Site location is best for a sunny area with well-draining soil and preferably, southern exposure. Old agricultural fields or recently clear-cut patches are suitable and a soil test is performed to determine the nutrient content and see how much replenishment with fertilizer is needed. Most of these trees are started from seed, though grafted or transplanted sources may be used as well. Finding new sources to plant can take some time, and therefore somewhat difficult to predict exactly how many seed will be planted each year. As such, this type of orchard may take several years before fully planted. Annual meetings between CT-TACF and the orchard host will be held at least annually and will help to review the status of the project and also provide a mechanism for planning the upcoming year’s activities.
Successful orchard management tries to mitigate the major sources of mortality for the nuts and trees planted. These include but are not limited to: rodents, raccoons, turkeys, and bears eating the nuts; voles, mice, and deer eating bark or twigs; drought stress; competition from weeds; standing water; insect infestations; and mowing over trees. Trees that are well nourished and watered respond better to most threats than trees that are stressed. Successful orchards respond well to simple management practices, such as maintenance of fencing, periodic weeding, watering and fertilizing. In addition, accurate labelling, record keeping, and data collection are of great importance for tracking and future use of the trees for scientific purposes.
Land Trusts would be the ideal arrangement since the land, access, and purpose is traditionally already established. Two new GCOs planted in April 2021 have Land Trust ties.


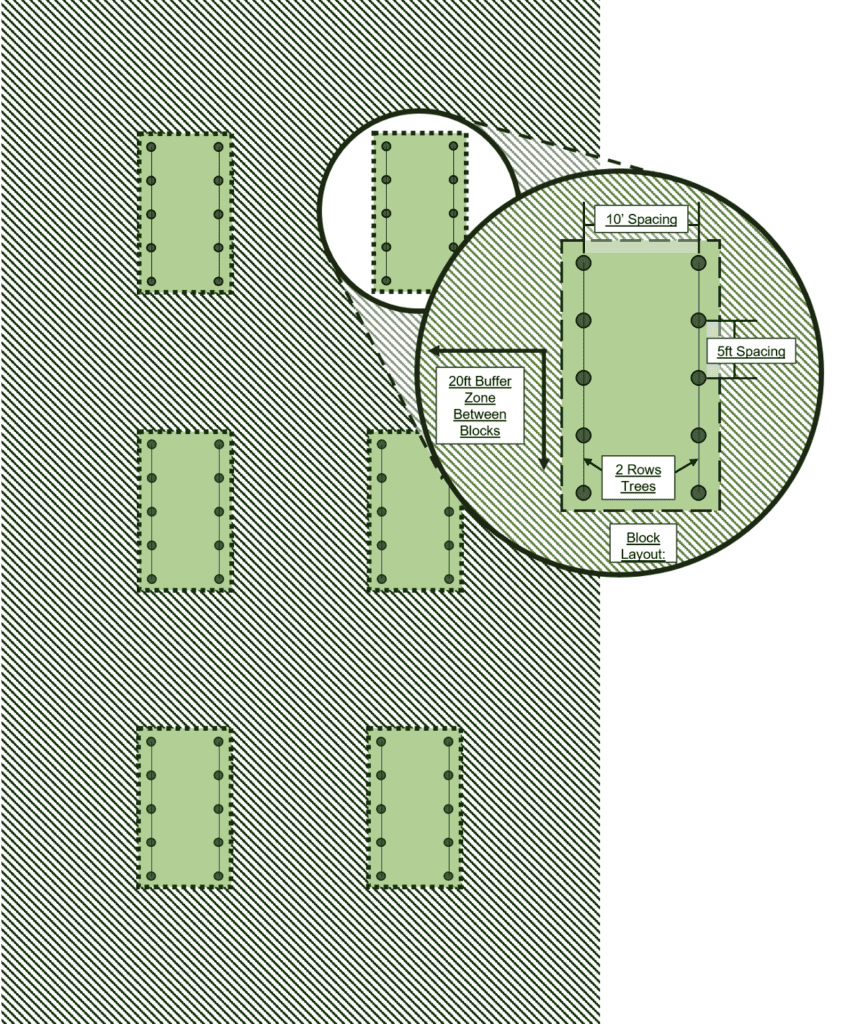
Suggested Layout
A blocked layout that keeps genotypes together is recommended. This is the simplest way to keep sources clear. A wide buffer between blocks allows for good pollination access. With this design, orchard managers will need to resist the urge to plant within the buffer rows, especially while trees are small. It is also important that any replacements are only made with the same genotype.
Pollination and Harvest
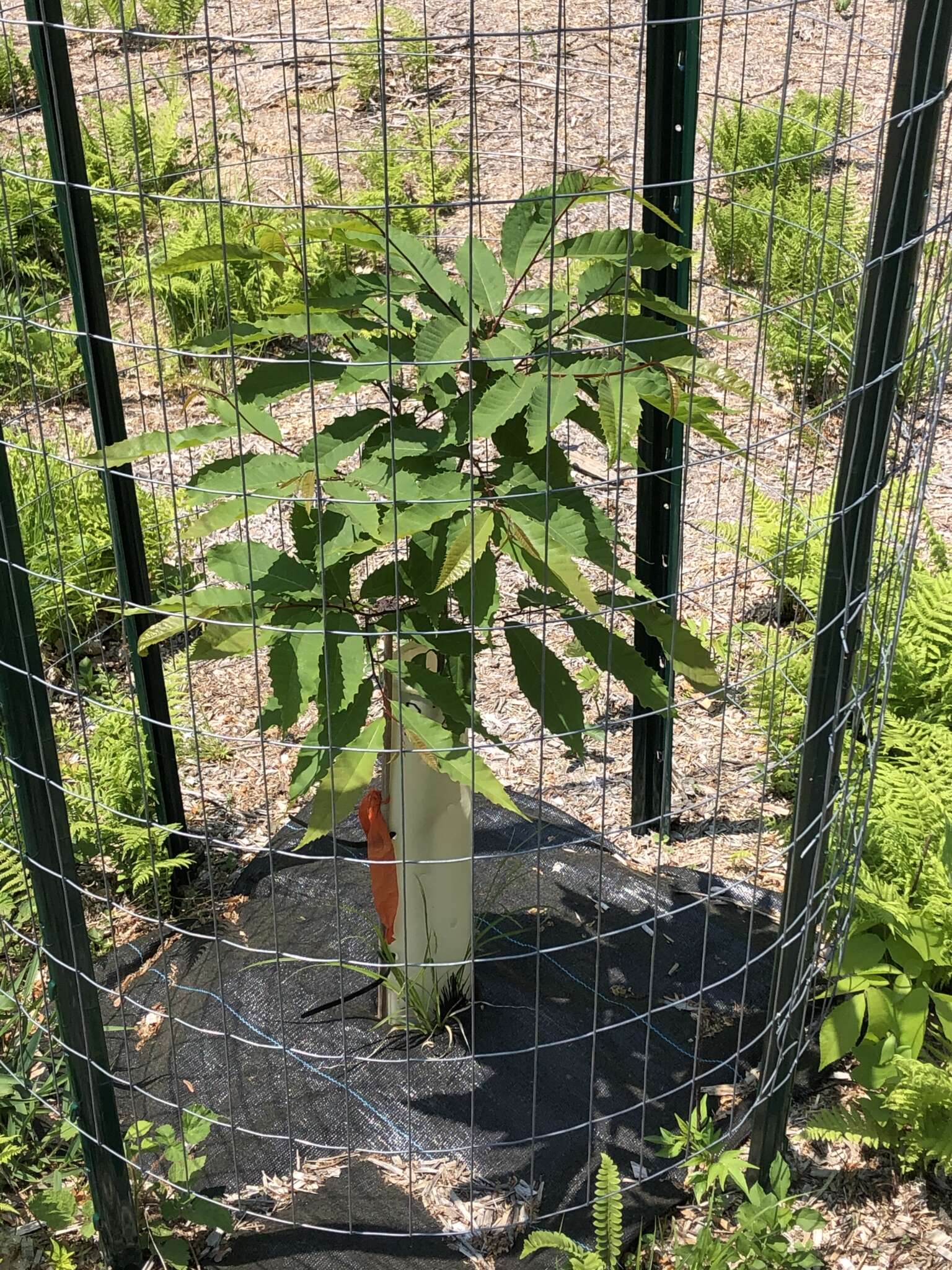
As trees grow old enough to begin flowering, they may be used for transgenic diversification or other crosses of interest. Chestnuts start flowering in June, with full bloom coming in early-mid July. For controlled pollinations, flowers are typically bagged in late June or early July, pollinated 10-14 days later, and harvested in late September or early October. Pollination requires working directly with the flowers and is typically done from a ladder or bucket truck, though small trees may be pollinated from the ground. As more trees begin flower the potential also exists for harvesting open-pollinated nuts. These may be used for TACF science programs, eating, or both.
Blight Control Measures
As wild-type American sources, the trees in a GCO are not expected to have any blight resistance and blight will eventually move through the orchard. Main stems will be killed over time and should be allowed to re-sprout. There are some methods that could be used to try to keep them alive longer. Mudpacking can be used and is most effective if cankers are caught early. Assessing the trees for blight annually (or more frequently), so mudpacking can be planned for, is helpful. Hypovirulence treatment is also a possibility, though not currently widely available.
Further Reading to Assess Expectations
A sample Orchard Management Plan
A sample CT GCO agreement
An article (page 15) from the Journal of the American Chestnut Foundation.
Interested parties should contact the Connecticut chapter for more details.

